Python分析冠状病毒基因组 | Biopython构建系统发生树,以冠状病毒基因组序列为例(COVID-19,SARS,MERS,EBOLA),最大似然估计法(ML)
系统发生树 定义
系统发生树(phylogenetic tree)是表明被认为具有共同祖先的各物种相互间演化关系的树
分类
- 是否有根?- 有根树:具有方向的树- 无根树:没有方向,其中线段的两个演化方向都有可能
- 基因树和物种树
构建方法
计算的精度和时间均依次增大
- 非加权分组平均法:UPGAM(Unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean)
- 矩阵法:邻接法 neighbor-joining (NJ)
- 简约法:最大简约法 maximum parsimony (MP)
- 似然法:最大似然法 maximum likelihood (ML)
- 后验概率法:贝叶斯法 Bayesian
用什么序列建树?
- 如果DNA序列两两间一致度大于70%,选用DNA序列
- 低于70%选用蛋白质序列或DNA序列
What is the difference between a guide tree and a true phylogenetic tree?
A guide tree is calculated based on the distance matrix that is generated from the pairwise scores. The output can be found in the .dnd file. A phylogenetic tree is calculated based on the multiple alignment that it receives. The distances between the sequences in the alignment are calculated and can be found in the .ph file. These distances are then used by the method chosen (nj, phylip, dist) to make the phylogenetic tree (.nj, .ph, .dst file).
from Bio import SeqIO ## 导入模块
## 读入序列数据covid = SeqIO.read('data/covid19.fasta', 'fasta')sars = SeqIO.read('data/sars.fasta', 'fasta')mers = SeqIO.read('data/mers.fasta', 'fasta')ebola = SeqIO.read('data/ebola.fasta', 'fasta')
## 合并文件all_virus = [covid, sars, mers, ebola]SeqIO.write(all_virus, 'data/all_virus.fasta', 'fasta')
4
## 数据来源 GenBank## 打印数据信息for i in all_virus:print('%s\t%s' % (i.id, i.description))
NC_045512.2 NC_045512.2 Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 isolate Wuhan-Hu-1, complete genome
NC_004718.3 NC_004718.3 SARS coronavirus Tor2, complete genome
NC_019843.3 NC_019843.3 Middle East respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus isolate HCoV-EMC/2012, complete genome
NC_002549.1 NC_002549.1 Zaire ebolavirus isolate Ebola virus/H.sapiens-tc/COD/1976/Yambuku-Mayinga, complete genome
## Alignment## 进行对齐/序列比对
from Bio.Align.Applications import ClustalwCommandline
cline = ClustalwCommandline('clustalw', infile='data/all_virus.fasta')
stdout, stderr = cline()
## 输出文件将保存在源路径下: all_virus.aln all_virus.dnd%ls data
all_virus.aln all_virus.fasta ebola.fasta sars.fasta
all_virus.dnd covid19.fasta mers.fasta
## 可以用Bio.AlignIO读取输出结果from Bio import AlignIO
align = AlignIO.read('data/all_virus.aln', 'clustal')
print(align)type(align)
Alignment with 4 rows and 30972 columns
ATTAAAGGTTTATACCTTCCCAGGTAACAAACCAACCAACTTTC…AAA NC_045512.2
ATATTAGGTTTTTACCTACCCAGGAAA–AGCCAACCAACCT-C…— NC_004718.3
-------GATTTAAGTGAATAGCTTGGCTATCTCACTTCCCCTC…— NC_019843.3
--------------------------------------------…— NC_002549.1
Bio.Align.MultipleSeqAlignment
## 写出为phylip格式AlignIO.write(align, 'data/all_virus_align.phy', 'phylip')
1
## 可以用Bio.Phylo读取树文件from Bio import Phylo
## clustalw 生成的 guide treeguide_tree = Phylo.read('data/all_virus.dnd', 'newick')
Phylo.draw_ascii(guide_tree)
__________ NC_045512.2________________________|| |__________ NC_004718.3_||___________________________________ NC_019843.3||_________________________________________________________________ NC_002549.1
## 建树from Bio.Phylo.Applications import PhymlCommandline
## 调用Phyml,以ML法生成系统发生树cmd = PhymlCommandline(input='data/all_virus_align.phy')out_log, err_log = cmd()
## 生成树文件和统计文件%ls data | grep .txt
all_virus_align.phy_phyml_stats.txt
all_virus_align.phy_phyml_tree.txt
tree = Phylo.read('data/all_virus_align.phy_phyml_tree.txt', 'newick')
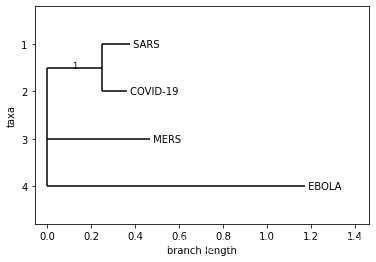
## 自定义labellabels = {covid.id[:10]: 'COVID-19',sars.id[:10]: 'SARS',mers.id[:10]: 'MERS',ebola.id[:10]: 'EBOLA',None: None}
Phylo.draw(tree, label_func=lambda a:labels[a.name])
其他
对齐和建树的时候,python分别调用了外部程序:clustalw和phyml,
可从bioconda安装:
conda install bioconda::clustalw
or
conda install -c bioconda phyml

